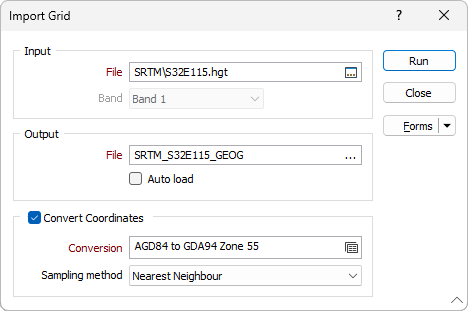
Import Grid (Raster) Data
![]()
Input file
Click the ellipsis button to navigate to the location of the input grid file. A wide number of third-party grid file formats are supported. The same formats can also be opened as images in Vizex.
Band
In the case of a multi band dataset, only ONE band can be imported. When multiple bands are detected, the Band selection drop-down list is enabled. The first band is selected by default.
64-bit data cannot be converted into 32-bit Micromine Australia Pty Ltd Grid format. If you want to import 64-bit data, you must first use GIS or image processing software to re-scale the data to 32-bits or less.
Output file
Enter the name of the Grid (*.GRD) file that will be created as a result of the import process. If you do not select a location, the file will automatically be saved to the same folder as the input file. To overwrite an existing file, double-click (F3) to navigate to the location of the file.
You can also display the same grid formats directly in Vizex by loading them via Display | Grid File.
Auto load
To display the data in Vizex once the file(s) have been imported, select the Auto load option.
Convert Coordinates
Select the Convert Coordinates check box to convert between geographic coordinates (latitudes and longitudes) and projected or local coordinates, as part of the import process.
Conversion
Select, or create a new, coordinate conversion form set. See: Coordinate System Conversion
Sampling method
Select a sampling method:
| Method | Input Cells | Calculation | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Nearest Neighbour |
1 (1 × 1) |
Returns the nearest cell value |
|
|
Bilinear |
4 (2 × 2) |
Combined linear interpolations along the X and Y axes |
|
|
Cubic |
16 (4 × 4) |
Cubic convolution |
|
|
Cubic Spline |
|
Piecewise cubic polynomial |
|
|
Lanczos |
|
Windowed sine cardinal (Sinc) function |
|