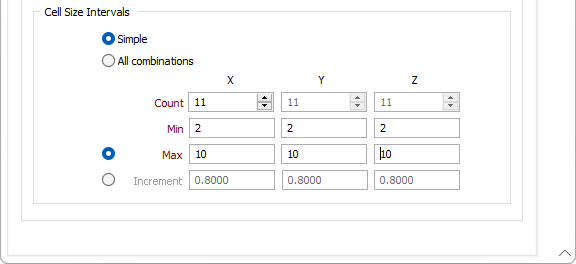
Grid
On the Grid tab of the Cell Declustering form, set the grid orientation, origin, cell size and extents.
Specify Origin
You can either explicitly specify the origin of the grid in the X, Y and Z fields or, when no origin is specified, let the function auto calculate the origin.
Dither Origin
Because the optimum virtual block size for 3D block declustering is not known in advance, an iterative approach is used to determine the optimum size. You define the number of iterations by cell sizes or increments. To avoid erratic results caused by outliers at the edges of the data, optionally enable the Dither Origin option to shift the virtual block origin grid origin for each cell size.
Once the iterations are complete, simply read the mean and standard deviation of the chosen iteration by selecting the corresponding point in the chart. When high grades are preferentially sampled, which is typical for the primary elements of most ore deposits, the lowest mean is the declustered mean. The opposite may be true for penalty elements: when low grades are preferentially sampled, the highest mean is the declustered mean. However, if the calculated mean seems too low (or too high), choose a value from a less aggressive iteration.
Grid Orientation
- Use angles
Enter Azimuth, Plunge, and Rotation values to define the orientation.
- Use ellipsoid
Click the Forms icon to select a search ellipsoid and use its orientation. See: Ellipsoid Parameters
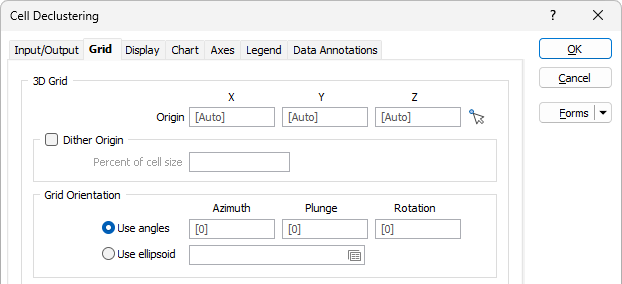
Cell Size Intervals
Specify the X, Y and Z cell size of the grid and the number of intervals which determine the iterations shown in the chart.
Select the Simple option to use only the X values to calculate the cell size of the clustering grid. Select All combinations if you want to use the X, Y and Z values.
Select the Max option to define the maximum cell size to end with, or select Increment to auto calculate the Max values to be (Min + Increment * Count). The iterations will be created so that the first has the Min cell size, the last has the Max, and the ones in between will linearly interpolate between Min and Max.