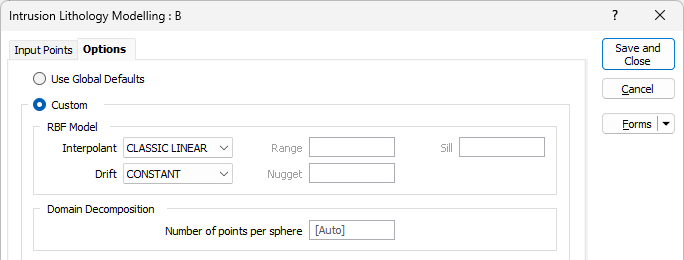
Options
The Options tab of the Intrusion Lithology Modelling form contains options and settings for RBF Model, Domain Decomposition, Weighting, and String Conditioning for your model.
You can select the Global Defaults option to use the global lithology defaults, or select Custom to define the settings for this model.
RBF Model
To generate a realistic implicit model, it is essential to restrict the effect of each drillhole sample to the surrounds of its local region. This is achieved using Interpolant functions which have similar options to variograms for range, sill, and nugget.
| CLASSIC LINEAR | The standard linear kernel. |
| LINEAR | A linear kernel with an option for a nugget. The slope is defined by the ratio (Sill - Nugget) / Range, whilst the effect of the nugget is controlled by the ratio Nugget / Sill. |
| Nugget is simulated by adding a small Gaussian component to the kernel, which has the tendency to produce more lumpy surfaces at each data point. |
Using a non-zero nugget leads to longer processing times.
Drift
Drift determines how the value distribution is modelled further away from the sampled data:
| NONE | The interpolant decays to zero. |
| CONSTANT | The interpolant assigns a constant value which is an approximation of the mean of the data. |
| LINEAR | The interpolant varies linearly. |
Range
If you have chosen the LINEAR interpolant, enter a Range value.
The exponential variogram never reaches the sill. The range is the point where the variogram reaches 96% of its sill value.
Nugget
If you have chosen the LINEAR interpolant, enter a Nugget value. The Nugget value (effect) is the variance at distance zero. This is always less than the sill. The nugget effect arises because the regionalised variable is erratic over a very short distance that that the semi variogram goes from zero to the nugget effect in a distance less than the sampling interval.
Sill
If you have chosen the LINEAR interpolant, enter the Y coordinate (semi variogram) value of the sill for each component of the model. This is constant for a dataset.
Points/Sphere
In most cases it is impractical to create a single model using all the points in the data set. Instead, the data set can be divided into overlapping regions. These regions are defined by the direction of propagation of spheres across the input data:
The Points/Sphere value is the number of points you want to look at per sphere. The radius of each sphere will therefore depend on the concentration and the distribution of the points in the input data.
This value is calculated automatically based upon the input data. Unless a number is entered, the field defaults to [Auto].
Domain Decomposition
In most cases it is impractical to create a single model using all the points in the data set. Instead, the data set can be divided into overlapping regions. These regions are defined by the direction of propagation of spheres across the input data:
The Number of points per sphere is the number of points you want to look at per sphere. The radius of each sphere will therefore depend on the concentration and the distribution of the points in the input data.
This value is calculated automatically based upon the input data. Unless a number is entered, the field defaults to [Auto].
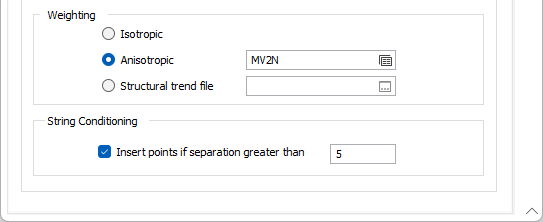
Weighting
Select a Weighting option:
- When you select an Isotropic orientation method, there is no preferred direction.
- When you select an Anisotropic orientation method, you enter a preferred direction, as well as specify the weighting in that direction.
- When you select Structural Trend File, a data search weighting is derived from the direction of anisotropy defined in a (*.mmstf) Structural Trend File, which is an output of the Implicit Modelling | Structural Trend | Create Trend function.
Double-click to load an existing form set. Alternatively, right-click in the Anisotropic input box to open a form where you can define the shape and direction of the search ellipsoid.
The ability to apply a weighting based on the orientation of a data search ellipsoid is a useful option. Although it references the same set of parameters used to define a data search for block modelling, only a few of the values are utilised by implicit modelling.
For example, only the factors and rotation associated with the orientation axes are used – the radius is ignored and will be greyed out. If you consider that there is a greater correlation in one direction in particular, select Ellipsoidal, and set appropriate factor, azimuth, plunge and rotation values.
This effectively accounts for any anisotropy. Interpolation weights can be adjusted accordingly; data points located along the major semi-axis will receive a higher weighting than those located along the minor semi-axis, for similar distances from the prediction location.
String Conditioning
Insert points if separation greater than
Select the option to specify a maximum separation between points value in order to insert points where necessary to make the segmentation of the string more uniform. As a result, a wireframe generated from the string will be smoother.
Click the Save and Close button when the lithology Modelling form is completed, to return to the Surface Map.