Import
![]()
More often, you will want to merge external data with matching data in a data file in the program. For example, merging assay samples with field location. With Merge you do not have to import all the fields in the source file nor are you committed to the field order in the source file.
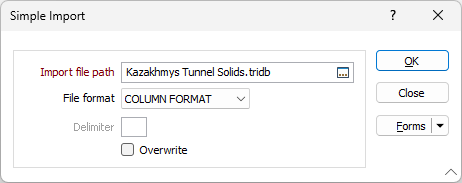
Import filepath
Enter the name and location of the file of interest in Import filepath. If you double click (F3), the Windows™ Select File dialog box will open. Use this to select an external file. Once you have selected a file, you can right double click (F4) to view its contents. This is limited to the specified file types.
File format
Choose a (COLUMN, DELIMITED, TAB, SPACE, COMMA, SEMICOLON, PIPE) delimited file format from the drop down list.
Delimiter
If DELIMITED is selected as the file format, enter the ASCII value of the delimiter.
Overwrite
(Optional) Select this option if you intend to overwrite data in the current file (the file into which the data will be imported).
OK
Finally, click the OK button to begin the import process. A message box appears listing the name of the file being imported and the name of the target file. Click the OK button if these are correct. If not, press ESC to interrupt the process. A message will be displayed when the process is complete. If an error occurs, an error message will be displayed.
When data is stored in exponential notation e.g. 0.12340000E3, import the number then convert it back to normal notation i.e. 123.4 by multiplying it by 1 using the Calculate tool on the File | File Editor tab, in the Edit Fields group.
If you import data from the same source often, use a Form to save the entries in the Import form for later use.