Fields
A Leaf is defined as the overall data container at the lowest Level in a Level/Position tree structure. Each of these Leaves can contain anywhere from one to a great many number of individual pieces of data. Since different types of data are stored in different ways (dates and percentages, for example, are stored and reported differently) fields are required.
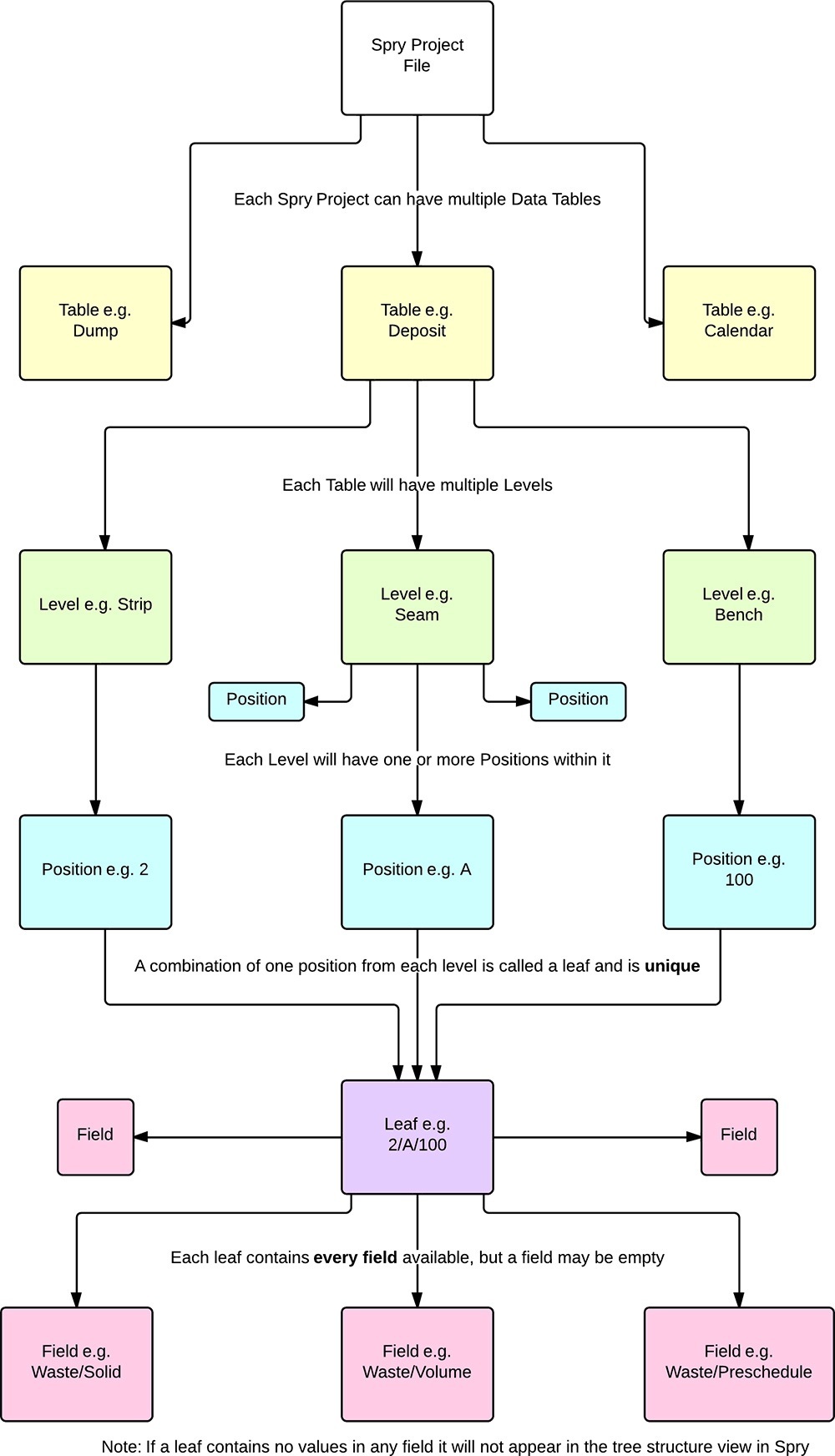
In Micromine Spry, there are eight different types of Fields:
- Numeric (Double Precision Float): Any number including decimal places. Common examples include physical properties (Area, Thickness, Volume, Tonnes etc.) and equipment rates
- Numeric (Percentage): For when your data is a percentage. Common examples include qualities, preschedules and availability/utilisation.
- Numeric (64-bit Integer): Any number but does not accept decimal places. No common examples, technically available for particularly large (>16 digit) whole numbers.
- Text String: Can contain any data (as a string) but no mathematical operations can be performed. Commonly used to preserve data for reporting/auditing purposes.
- Date/Time: Calendar tables make use of this for various dates (e.g start and end dates).
- Point3D: A single point in 3D space with X, Y and Z positions. Common examples are roof, floor and volumetric centroids.
- Solid: Geographical modelling solids are kept in Solid data types.
- Bool: True or false. Commonly used for "flags".
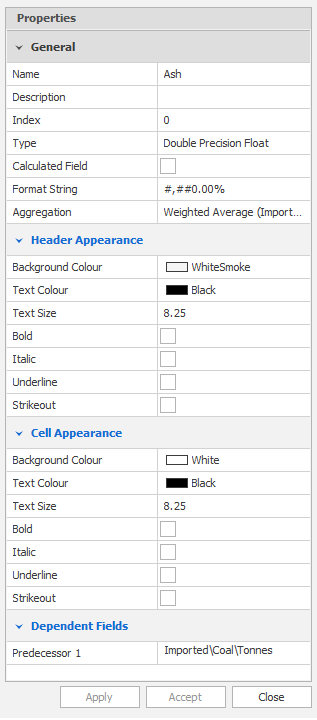
Besides a Type, a Field also has several other properties, primarily relating to how they are displayed in Table View and in various results:
- Name: Must be unique in the Table and generally describes the data contained within in a simple way. An example would be Imported/WasteVolume
- Description: Used primarily for auditing purposes, has no application other than as a more verbose description in the Fields view in the application.
- Format String: This controls the way the field appears, but does not affect the actual data storage (you can display a number 0.532 as 0.53 but the number stored remains 0.532). The Format String nomenclature is based on C# standards. For a summary, see: Format Strings
- Aggregate: The controls the way data is summarised when displayed at a higher Level than the lowest. Aggregation can be None, Minimum, Maximum, Sum, Average or Weighted Average.
- Weighted Field: When Weighted Average is chosen as the Aggregate, this is where you choose another Field to weight it with.
- Header and Cell Appearance: Controls the colour, size and appearance of folders and fields in Table View.
Once the Fields and Levels & Positions are set up, you are now in a position to import your data. See: Data
Calculated Fields
Calculated Fields allow for Field Values to be based on an Expression as opposed to being imported or based on a script. Calculated Fields can reference other Fields within the same Leaf, and can be based on the current Levels and Positions. You can also reference values on other Tables using the TableValue Function, but it's important to know that you cannot currently reference other Positions within the current Table.
For more information, see: Calculated Fields
If you are not already familiar with Expressions, see: Example Expressions

Add Fields
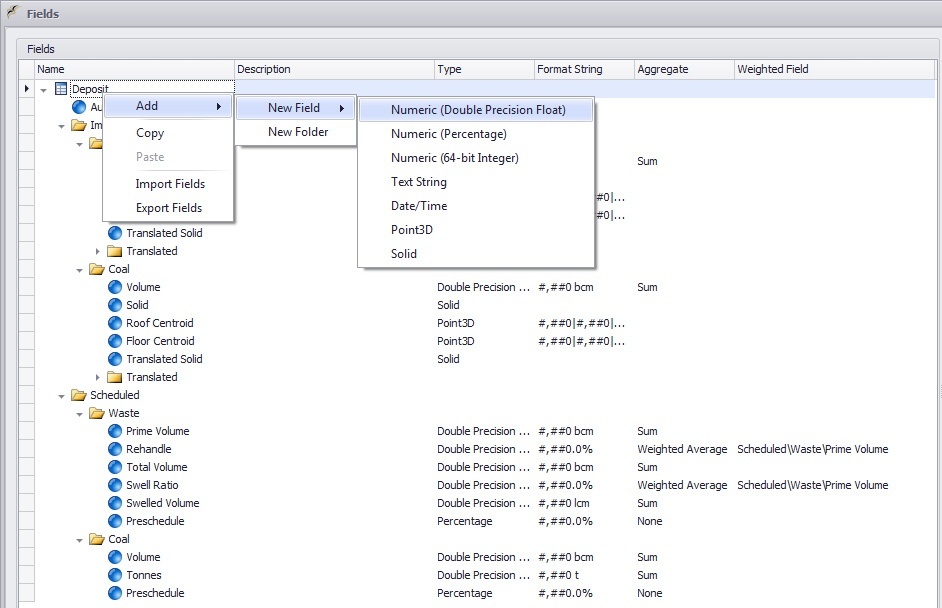
To create a field, right-click Table in the Project Explorer and choose Setup Fields.
Each Field can be added by right-clicking the Table name or a folder, and left-cliking the Type you want from the menu option.
Note: When created, every Field defaults to an empty or 0 state. In addition, once a Field is created you cannot change the type.
The Format String nomenclature is based on C# standards. For a summary, see: Format Strings
Other display formatting options appear in the Properties window on the right hand side of the Fields window.
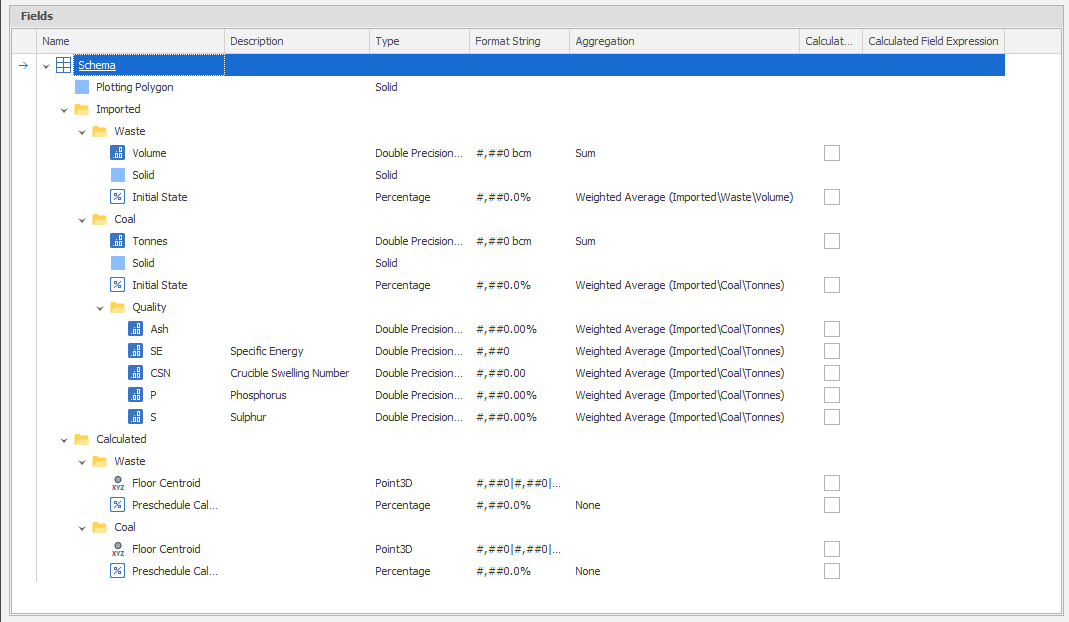
Calculated Fields
Note: Ticking on "Calculated Field" will wipe any existing Data present in the Field. See: Calculated Fields
Common Functions and Expression parts:
- GetValue(): Use this to reference other Fields in the same Leaf
- Level=LevelPosition: For example Pit=PitAlpha as part of an If() Function