Replaceable Parameters
If you want to execute the same form with different input, you can save several forms, and call each one with a macro instruction. However there is a more efficient way; replaceable parameters.
Replaceable parameters enable you to setup a form once and then use it repeatedly in a macro with different input parameters. For example, the section coordinate when you are generating multiple sections. You can take two different approaches depending on what you want to achieve:
- Pass parameters.
- Substitution parameters.
Pass parameters
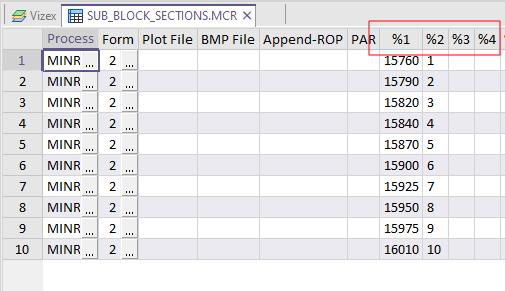
Pass parameters operate on saved form sets. To use them you must setup the form with the data that is to remain fixed. For each parameter you want to change, type in one of the pass parameters %1 to %99, instead of a fixed value.
You will need to modify the file to create additional macro fields %1 to %99 yourself. The numbers MUST be consecutive.
When you call the form from the macro, the values in the corresponding Par fields (%1 to %99) in the macro record are passed to the function. You still have to use a macro instruction for each execution of the form, but you only have to set up the form once.
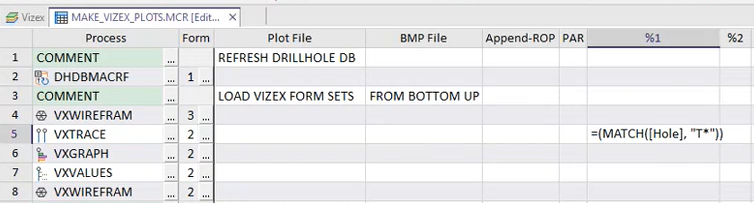
Expressions are also supported when specifying macro replaceables. For example, to filter out the holes in a drillhole display to only show trenches, instead of going into the underlying form and setting an expression on the filter, you can now type %1 in the filter field, save the form and then enter the expression directly in the %1 field in the Macro Editor:
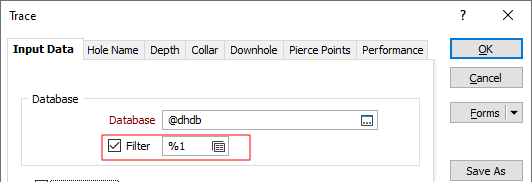
Replaceable pass parameters can also be used as Expression Variables.
Substitution Parameters
Substitution parameters operate on macro files. To use them you must create a table of codes and corresponding values in Macros | Substitution Table. The substitution table consists of 34 rows. It has a column of codes (@) and corresponding values (Substitution). Once you have filled out this table, save it as a form set for the MACSUB function.
The substitution values defined in the MACSUB form apply to all subsequent records in the macro file - until another MACSUB function is entered.
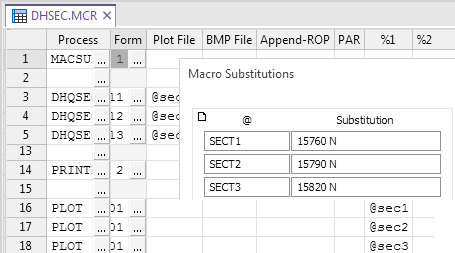
Substitutions can also be used directly in a form. For example, a Database Name substitution that can be used in multiple forms:
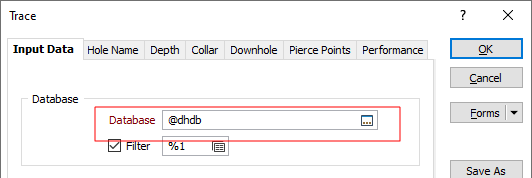
Note that you can also reference predefined substitution parameters (or the project substitutions you define yourself) in expressions or enter them directly in a form. See: Project Substitutions and Predefined Substitution Parameters