Coal Washability Analysis
Coal Beneficiation
Coal is a combination of organic material and mineral matter. The inorganic material does not burn and remains as a residue in the furnace.
This is also known as the ash content of the coal. There is a direct relationship between the ash content and the relative density of coal. Coal beneficiation is based on a density separation process that effectively washes out the heavier inorganic material .
Washability Analysis
- Float and sink testing is the standard laboratory method for determining the washability characteristics of coal.
- When immersed in a tank containing a liquid with a predetermined relative density, a portion of the sample material will float, while the remainder will sink.
- Using a series of tanks with varying RD values, the original sample is divided into several float fractions and a final sink fraction.
- The proportion of each fraction is expressed as a percentage of the total sample mass (also known as the fractional yield).
- The material from each individual fraction is subjected to laboratory testing in order to determine the ash content and other characteristics of the coal for the corresponding RD range.
Coal Analyses
Typical parameters included in washability analyses are:
- Mass yield, representing the portion of the sample that floated at a specific relative density
- Ash content
- Volatile matter
- Inherent moisture
- Fixed carbon (100 ash volatiles moisture)
- Heat value (calorific value or specific energy)
- Sulphur and phosphorus
Additional analyses
- Ash analyses (breakdown of inorganic chemistry)
- Ash fusion temperatures (important for furnace design)
- Coking properties (important for metallurgical use)
- Several physical properties
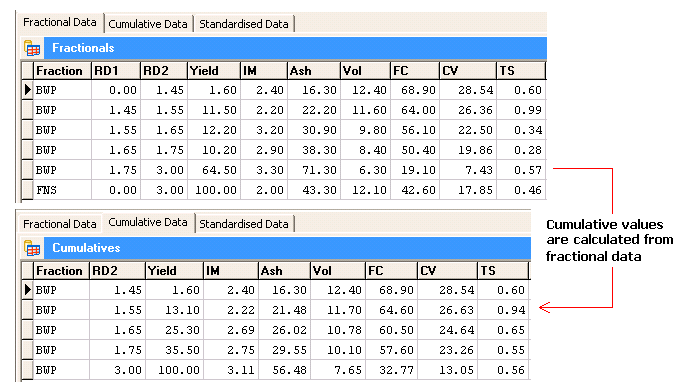
Cumulatives
Cumulative floats are calculated by combining the results of individual float fractions, using a system of weighting based on the mass yield.
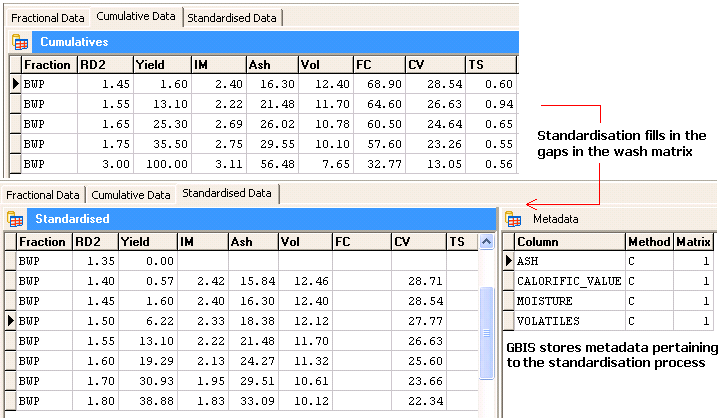
Standardisation
Standardisation is the process whereby the original cumulative matrix is expanded to deliver a regular (usually more comprehensive) washability matrix.
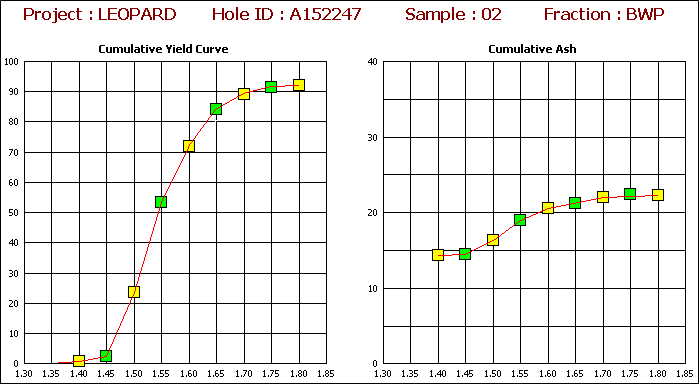
Interpolation
The missing values (yellow) are interpolated from spline curves fitted to the original cumulative data points (green).
Equations
Where the unknown point falls outside the range of data points, extrapolation is based on a system of user-defined Washability Equations.